|
Back Lesson 3
|
Home Cover Page
|
Top Lesson 4
|
Next Lesson 5
|
Lesson Four: Demonstration of Osmosis in Living Cells using Potato
Materials required: Potato tubers (cylinders), razor /blade/, salt solution, distilled water, Petri dishes, ruler, absorbent tissue. A chart illustrating osmosis.
The teacher may use different ways of introducing the lesson. He/ she may use the method of activating background knowledge. For example he/she can review the previous lesson by asking the following questions.
The above questions help to engage students and they stimulate for active participation. The teacher may expect possible answers as follows.
Diffusion is the movement of molecules from a region of high to a low concentration until equilibrium is reached. Substances move down concentration gradient in diffusion. Diffusion is a passive process (does not require energy). There are different mechanisms of transport of substances in living organisms or in cells. These are simple diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion and active transport. We need to transport substances for cells’ metabolic activities and regulation of the internal environment. Cells need oxygen and different nutrients for sustaining life. Conversely, metabolic waste products are not needed by cells and they should be removed from cells.
The teacher should organize the learners into groups and guide learners. The learners are required to set up the experiment on osmosis using the procedure below.
Procedure
Complete the calculations in figure below using the formula provided.
% Change in length = (change in length × 100) / Initial length
Change in length = Final length - Initial length
Note: The change in length may be negative in some cases whenever there is a loss of water.
|
Distilled water |
NaCl |
||
0.1% |
10 % |
50% |
||
Initial length (cm) |
|
|
|
|
Final length in (cm) |
|
|
|
|
Change in length (cm) |
|
|
|
|
% change |
|
|
|
|

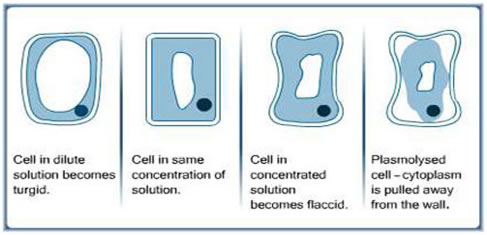
Fig 4.1 Plant Cells Surrounded by Different Solutions
Note: Osmosis is solely used for describing movement of water molecules only. Sometimes students described osmosis as the movement of water potential rather than the movement of water molecules.
Always remember that water potential is a measure of the tendency of water molecules to move from one place to another. A dilute solution contains more water molecules per unit volume than a concentrated solution so it has a higher water potential than a concentrated solution
The teacher is expected to evaluate the success of the lesson. As this lesson is a practical activity, students are expected to prepare a report of their practical investigation for the next class. Actually, the following questions can be formulated to enable students draw conclusions from their experiment.